In today’s fast-paced software world, the push for speed and efficiency has given rise to Low-Code/No-Code (LCNC) testing tools. These platforms make automation accessible beyond traditional coders, enabling testers, business analysts, and other stakeholders to actively contribute. From drag-and-drop test creation to AI-powered maintenance, LCNC tools simplify and accelerate testing while reducing skill barriers. However, they also bring challenges around flexibility, scalability, and vendor lock-in making it essential to weigh their benefits and trade-offs carefully.
Introduction
In the fast-paced world of software development, the demand for speed, efficiency, and broader participation in quality assurance has never been higher. This relentless pursuit has fueled the emergence and rapid adoption of Low-Code/No-Code (LCNC) platforms, a trend now significantly impacting the domain of software testing. Once the exclusive playground of seasoned coders, test automation is increasingly becoming accessible to a wider audience, thanks to these innovative tools. But what exactly are they, and what are the trade-offs involved in their adoption?
What are Low-Code Testing Tools and No-Code (LCNC) Testing Tools?
Low-Code/No-Code testing tools are platforms that allow users to create automated tests with minimal to no manual coding.
- No-Code Testing tools typically offer a visual, drag-and-drop interface, pre-built components, and record-and-playback functionalities. Users interact with graphical elements to design test cases, often without writing a single line of script.
- Low-Code Testing tools provide similar visual interfaces but also offer the flexibility to inject custom code (e.g., in Python, JavaScript, C#) for more complex scenarios, integrations, or custom assertions that aren’t covered by the visual builder.
The core idea behind both approaches is to abstract away the underlying code complexity, making test automation creation faster and more accessible to individuals who may not have deep programming expertise, such as business analysts, manual testers, or even subject matter experts.
Common Low-Code/No-Code Testing Tools
With a clear understanding of what low-code/no-code tools are, it’s helpful to know some of the key players in this space. While the market is constantly evolving, several platforms have established themselves as popular choices for their ease of use and powerful features.
Here are some of the most widely recognized LCNC testing tools, each with a unique focus:
UI & Functional Test Automation
- Selenium IDE – A simple record-and-playback tool that lets testers create and run browser-based automation scripts without coding. Best for quick web automation POCs.
- Katalon Studio – An all-in-one low-code platform supporting web, API, mobile, and desktop automation with a user-friendly interface.
- Testim.io – AI-powered codeless test automation tool that creates stable, maintainable UI tests with self-healing locators.
- Ranorex Studio – Offers drag-and-drop test creation for web, desktop, and mobile apps, ideal for teams with mixed coding skills.
- Leapwork – A visual flowchart-based automation tool that simplifies test creation for complex systems and business workflows.
- Tosca (Tricentis) – A model-based testing tool that provides end-to-end enterprise automation for regression, functional, and risk-based testing.
- Functionize – Cloud-based AI testing platform that enables scriptless web testing with natural language input.
API Testing
- Postman – A popular tool for designing, testing, and automating REST and SOAP APIs with reusable test collections.
- Katalon Studio – Provides integrated API testing alongside UI automation with low-code test creation.
- SoapUI (ReadyAPI) – A no-code tool for functional, security, and load testing of APIs with advanced configuration.
Mobile Testing
- Appium Studio (Experitest) – Enhances Appium with a no-code interface for quick mobile app automation on real devices.
- Perfecto – A cloud-based test automation tool that enables scriptless mobile and web testing at scale.
- Kobiton – Provides AI-assisted scriptless mobile automation and real-device cloud testing for faster execution.
Codeless Automation Platforms
- ACCELQ – A natural language-driven test automation tool for web, mobile, API, and desktop applications.
- TestProject (by Tricentis) – A free, community-powered platform that supports scriptless web, mobile, and API testing.
- UiPath Test Suite – Combines RPA and codeless test automation using workflow-based test creation.
- Mabl – A low-code intelligent testing tool with auto-healing tests for web and API automation.
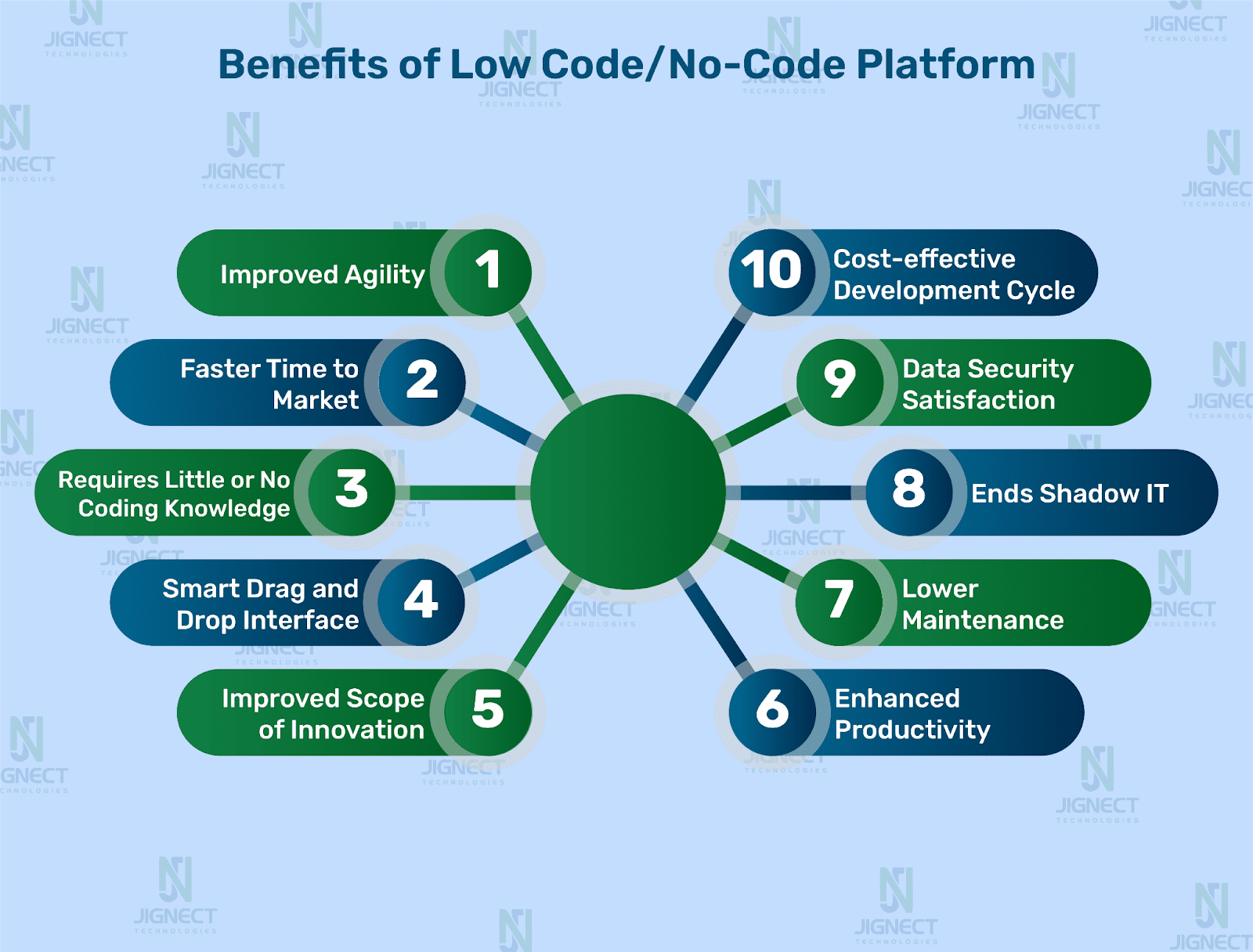
Advantages of Low Code/No-Code Testing Tools
The benefits offered by low-code/no-code testing platforms are compelling, particularly for organizations looking to scale their automation efforts quickly.
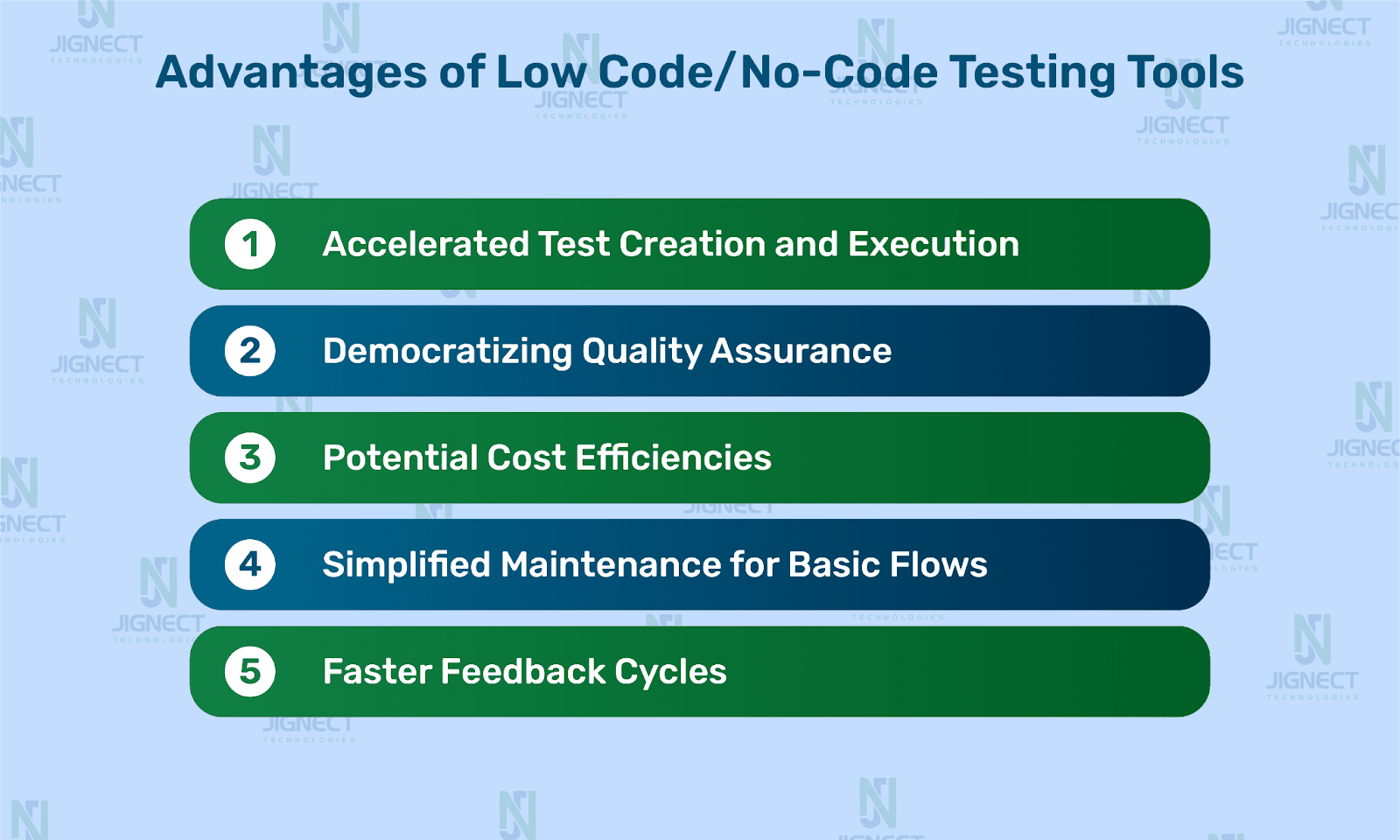
Accelerated Test Creation and Execution
One of the most significant advantages is the sheer speed at which tests can be built.
- Visual Interfaces: Instead of writing lines of code, users can drag-and-drop actions, define elements through point-and-click, or use record-and-playback features to rapidly build test flows. This drastically reduces the time from conceptualizing a test to having it ready for execution.
- Pre-built Modules: Many LCNC tools come with pre-built components for common actions (e.g., login, form submission, navigation), eliminating the need to write repetitive code for these actions.
- Faster Iteration: Test modifications are often as simple as rearranging visual blocks or updating element locators in a GUI, leading to quicker adaptation to application changes.
Democratizing Quality Assurance
LCNC tools bridge the skill gap, enabling a wider range of team members to contribute to automation.
- Empowering Non-Coders: Business analysts, manual QAs, and even product owners who understand the application’s functionality but lack coding skills can now design and maintain automated tests.
- Reduced Bottlenecks: This expands the pool of automation contributors, alleviating pressure on specialized automation engineers and allowing them to focus on more complex, challenging automation tasks.
- Increased Team Ownership: Quality becomes a shared responsibility across the development lifecycle, fostering a “whole team approach” to quality.
Potential Cost Efficiencies
While LCNC tools often come with licensing fees, they can offer long-term cost benefits.
- Lower Hiring Costs: Less reliance on highly specialized and expensive automation engineers for all tasks.
- Reduced Training Time: The intuitive nature of these tools often means a shorter learning curve for new users, translating to less training investment.
- Faster Time-to-Market: Quicker test creation and execution contribute to accelerated release cycles, potentially leading to faster revenue generation.
Simplified Maintenance for Basic Flows
Maintaining test suites can be notoriously time-consuming, but LCNC tools can ease this burden for certain scenarios.
- Visual Representation: Test flows are represented visually, making them easier to understand, even for someone who didn’t create the test. This simplifies troubleshooting and updates.
- Automated Element Handling: Many tools incorporate AI or smart locators that can adapt to minor UI changes, reducing the frequency of test breakage due to minor application modifications.
- Centralized Management: LCNC platforms often provide centralized dashboards for managing, scheduling, and monitoring test executions.
Faster Feedback Cycles
The speed of test creation directly translates to quicker feedback on code changes.
- Early Detection: Tests can be integrated into CI/CD pipelines more rapidly, allowing regressions or defects to be identified much earlier in the development process.
- Continuous Quality: This fosters a culture of continuous quality, where feedback is almost instantaneous, enabling developers to address issues while the context is still fresh.
Who Benefits Most from Low-Code/no-Code Testing Tools?
LCNC testing tools are not a one-size-fits-all solution, but they offer significant advantages for specific users and scenarios.
Citizen Testers and Business Analysts
- Empowerment: Individuals with deep domain knowledge but limited coding skills can directly contribute to test automation, ensuring tests align precisely with business requirements.
- Reduced Reliance: These tools free up highly skilled automation engineers to focus on more complex, technical challenges.
Teams Requiring Rapid Test Development
- Quick PoCs: For quickly validating new features or conducting proof-of-concept testing, LCNC tools allow for incredibly fast test creation.
- Short-Term Projects: Ideal for projects with tight deadlines or those that don’t require extensive, long-term, complex test automation suites.
Projects with Standardized UI Elements
- Predictable Interfaces: Applications with highly consistent, stable user interfaces and common interaction patterns are well-suited for LCNC tools, as element recognition is more straightforward.
- CRUD Operations: Applications primarily focused on Create, Read, Update, Delete (CRUD) operations, where UI flows are repetitive, can greatly benefit from the speed of LCNC.
Disadvantages of Low Code/No-code Testing Tools
While the allure of LCNC testing tools is strong, it’s crucial to understand their inherent limitations, which can become significant hurdles in complex environments.
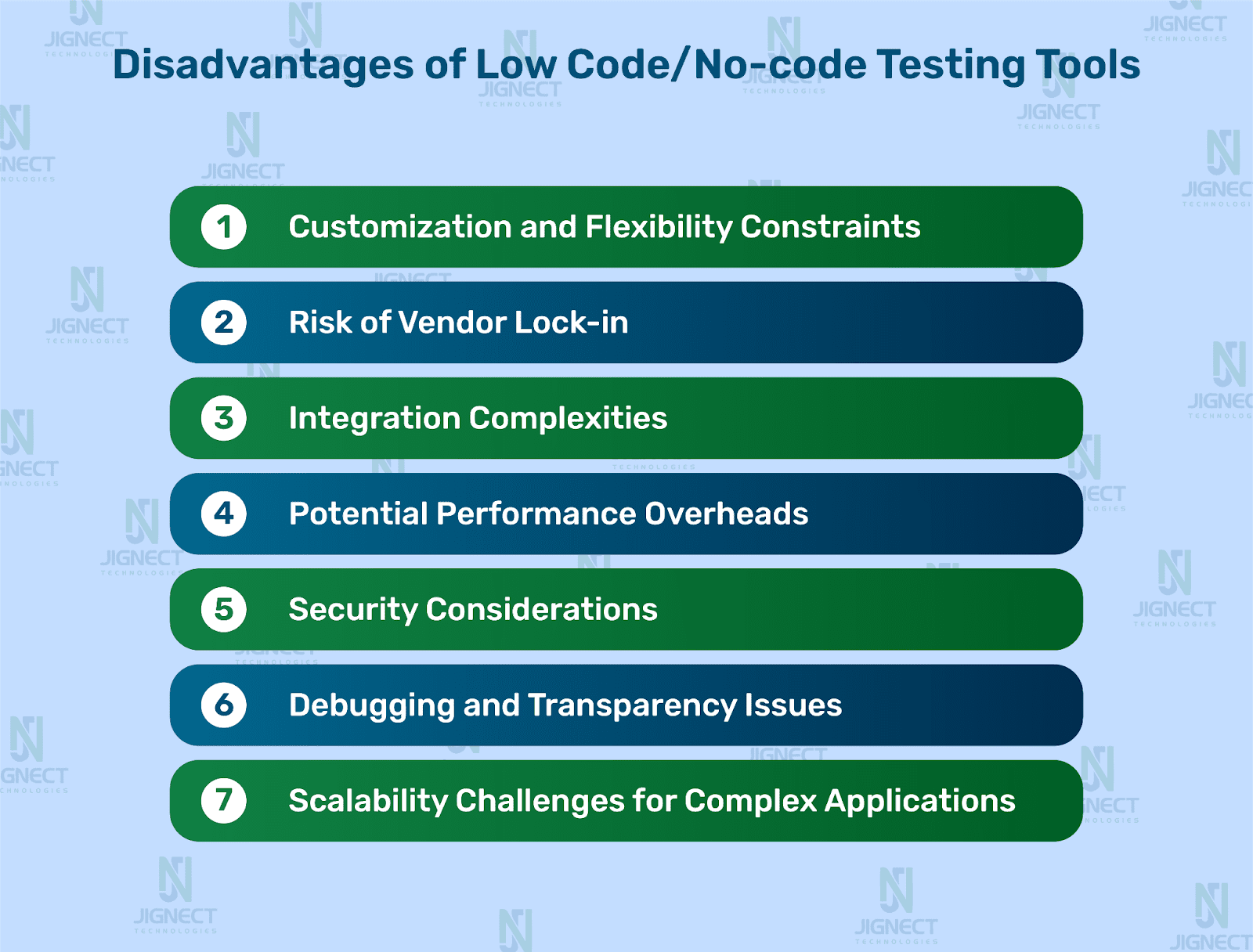
Customization and Flexibility Constraints
This is perhaps the most significant drawback.
- “Black Box” Nature: LCNC tools can sometimes act as a “black box,” making it difficult to understand or modify the underlying code logic generated by the tool.
- Complex Scenarios: Handling highly dynamic web elements, intricate data manipulations, advanced API integrations, or very specific testing edge cases often requires custom code that LCNC tools may not natively support, or which may be cumbersome to implement visually.
- Proprietary Frameworks: Tools may use their own proprietary logic or frameworks, limiting the ability to extend or integrate with external libraries.
Risk of Vendor Lock-in
Committing to an LCNC platform can make it difficult to switch later.
- Proprietary Formats: Tests created in one LCNC tool are often not easily portable to another tool or a custom automation framework.
- Migration Challenges: If a tool no longer meets your needs, or if costs become prohibitive, migrating your entire test suite can be a massive, costly undertaking, potentially forcing continued reliance on the original vendor.
Scalability Challenges for Complex Applications
While good for initial speed, long-term scalability can be an issue.
- Performance Overhead: The abstraction layers and visual engines used by LCNC tools can sometimes introduce performance overhead during test execution compared to lean, well-optimized coded frameworks.
- Test Data Management: Managing large, complex sets of test data might be less intuitive or powerful than with a coded solution that can leverage databases or external files more flexibly.
- Maintainability at Scale: For very large test suites with numerous interdependencies, managing test cases through a visual interface can eventually become unwieldy, potentially leading to “visual spaghetti” that’s hard to navigate and maintain.
Debugging and Transparency Issues
Troubleshooting issues in LCNC tests can be challenging.
- Limited Debugging Capabilities: Without direct access to the underlying code, diagnosing test failures can be difficult. Error messages from LCNC tools might be generic, obscuring the root cause.
- Opacity: It’s harder to inspect exactly what the tool is doing under the hood, making it difficult to optimize or understand unexpected behavior.
Integration Complexities
Connecting LCNC tools with existing CI/CD pipelines, reporting systems, or other development tools might not always be seamless.
- API Limitations: While some tools offer API access, it might be limited compared to what’s possible with a fully coded framework, hindering custom integrations.
- DevOps Ecosystem: Integrating LCNC tools into complex DevOps toolchains can sometimes require workarounds or additional manual steps, negating some of the efficiency gains.
Potential Performance Overheads
As mentioned earlier, the layer of abstraction can introduce a performance cost.
- Execution Speed: The visual interpretation and execution engines can sometimes make LCNC tests run slower than their traditionally coded counterparts. This can impact feedback loop efficiency, especially for large suites.
- Resource Usage: Some LCNC tools might have a larger memory or CPU footprint, requiring more robust build agents or infrastructure.
Security Considerations
While not a direct disadvantage of the testing process itself, reliance on third-party vendors for platform functionality inherently introduces a dependency.
- Data Handling: You’re entrusting your test data (which might include sensitive inputs) and potentially your application’s architecture details to a third-party platform. It’s crucial to vet their security practices.
- Platform Vulnerabilities: Any vulnerability in the LCNC platform itself could potentially impact the security of your test assets or even expose sensitive information.
The Driving Force Behind Their Popularity of Low Code/No-Code Testing Tools
The rise of LCNC testing tools isn’t a mere fad; it’s a response to several pressing industry needs:
- Accelerated Development Cycles: With Agile and DevOps methodologies dominating, releases are frequent, requiring tests to be created and updated at an unprecedented pace.
- Democratization of Testing: Organizations seek to empower more team members to contribute to quality, moving beyond a bottleneck of specialized automation engineers.
- Digital Transformation: As more businesses digitize their processes, the scope of applications requiring testing expands dramatically.
- Reduction of Technical Debt: LCNC promises to simplify the creation and maintenance of automation suites, reducing the burden of complex, brittle code.
- Focus on Business Logic: By handling the technical complexities, LCNC tools allow testers to focus more on validating business requirements and user flows.
When to Embrace and When to Be Cautious
Making the right decision about adopting LCNC testing tools involves a careful evaluation of your project’s specific needs, team’s skill set, and long-term vision.
Ideal Scenarios for LCNC Testing
- Rapid Regression Testing: For quick checks on common user paths after minor updates.
- Smoke and Sanity Testing: To ensure critical functionalities are working post-deployment.
- Non-Technical Teams: When the goal is to involve business stakeholders directly in test creation.
- UI-Centric Applications: Especially for applications with standard web forms and predictable navigation.
- Proof-of-Concept or Pilot Projects: To quickly demonstrate the value of automation without a large upfront coding investment.
When Traditional Coding Might Still Be Best
- Highly Complex or Dynamic UIs: Applications with constantly changing elements, complex AJAX interactions, or custom components that LCNC tools struggle to identify reliably.
- Extensive Data-Driven Testing: When tests require complex data generation, manipulation, or integration with diverse data sources.
- Deep Integrations: For scenarios requiring intricate API testing, database validations, or integration with specialized third-party systems.
- Performance Testing with High Load: While some LCNC tools offer basic performance checks, dedicated performance testing frameworks usually provide more control and accuracy.
- Long-Term, Enterprise-Scale Automation: When you need a highly customizable, maintainable, and scalable framework that can evolve with complex application landscapes over many years.
- Security-Critical Applications: Where full transparency and control over every line of test code is paramount.
Conclusion: The Future of Low-Code/No-Code Testing Tools
The rise of low-code/no-code testing tools is a significant evolutionary step in the software quality landscape. They are powerful enablers for rapid automation, democratizing testing and accelerating feedback cycles. However, they are not a silver bullet. Their inherent limitations in customization, flexibility, and scalability for highly complex scenarios mean that traditional coded automation frameworks still hold immense value.
The future of testing likely lies in a hybrid approach. Organizations might leverage LCNC tools for quick, straightforward UI regression tests performed by citizen testers, while relying on skilled automation engineers with coded frameworks for complex, critical, or performance-intensive scenarios. The key is to understand the strengths and weaknesses of both approaches and to strategically choose the right tool (or combination of tools) for the right job, ultimately driving higher quality software to market faster.
Witness how our meticulous approach and cutting-edge solutions elevated quality and performance to new heights. Begin your journey into the world of software testing excellence. To know more refer to Tools & Technologies & QA Services.
If you would like to learn more about the awesome services we provide, be sure to reach out.
Happy Testing 🙂




