In today’s fast-paced digital landscape, web app development isn’t just about writing great code, it’s also about ensuring that the application works reliably, securely, and as expected. This is where software testing plays a critical role. Whether you’re launching a SaaS product, an e-commerce platform, or a mobile-responsive web tool, thorough testing ensures a smooth user experience, better performance, and faster time-to-market.
Choosing the right testing approach manual or automated can significantly influence your product’s success. Not all testing needs are the same. Some demand human intuition, while others require speed and precision. Understanding these differences helps startups and businesses make smarter decisions when building and scaling web applications.
- What is Manual Testing?
- What is Automation Testing?
- Key Differences Between Manual and Automation Testing
- When Should You Choose Manual Testing?
- When Should You Choose Automation Testing?
- Cost and Time Considerations
- How to Strike the Right Balance (Hybrid Approach)
- Factors to Consider When Deciding Between Manual and Automation Testing
- Conclusion: What’s Right for Your Web App?
What is Manual Testing?
Manual Testing is a software testing process in which testers manually execute test cases without the use of automation tools. It relies on the tester’s perspective to verify that an application behaves as expected and meets user requirements.
Definition
Manual testing is the process of manually checking the functionality, usability, and performance of a web application by simulating user behavior. It involves going through each feature of the application, identifying bugs, and ensuring the UI and business logic are working as intended.
Common Use Cases
Manual testing is ideal for scenarios where human insight, intuition, and adaptability are required. Some common examples include:
- UI/UX Testing: Ensures visual elements render correctly across devices and browsers, and that user journeys are intuitive.
- Exploratory Testing: Performed without pre-defined test cases; testers explore the application on the fly to identify unexpected behavior.
- Ad-hoc Testing: Informal testing where testers use their knowledge to find defects not covered by formal test cases.
- Localization Testing: Checks how the application adapts to different languages and cultural contexts, often requiring human judgment.
Tools Used
Even though manual testing is performed without automation scripts, testers rely on several tools to track, document, and manage test cases and defects:
- JIRA – Popular for bug tracking, task management, and agile workflows.
- TestRail – A test case management tool used to plan, organize, and report on manual test executions.
- Xray – A JIRA plugin that helps manage both manual and automated tests.
- Zephyr – Another testing solution integrated with JIRA for test planning and execution.
What is Automation Testing?
Automation Testing is a software testing method that uses automated tools and scripts to execute test cases. It’s especially valuable when you need to run repetitive, data-driven, or complex tests efficiently and consistently without human intervention.
Definition
Automation testing involves writing test scripts that automatically check whether an application behaves as expected. Once these scripts are created, they can be reused multiple times, making the process faster and less error-prone than manual testing.
This approach is essential for improving speed, reliability, and test coverage, especially in continuous integration and delivery (CI/CD) pipelines.
Common Use Cases
Automation testing is best suited for:
- Regression Testing: Re-running existing tests to ensure new code changes don’t break existing functionality.
- Load Testing: Simulating a large number of users to check how the application performs under stress.
- Performance Testing: Measuring responsiveness, speed, and stability of the application under various conditions.
- Smoke and Sanity Testing: Quickly verifying basic functionality to confirm whether builds are test-ready.
Popular Tools
A variety of tools are available depending on your tech stack, project size, and goals. Some of the most widely used include:
- Selenium: Open-source framework for automating web browsers. Supports multiple languages like Java, Python, and C#.
- Cypress: Ideal for front-end testing, especially with modern web frameworks. Easy to set up and debug.
- Playwright: Microsoft-backed tool that supports modern web app testing with multi-browser support (Chromium, Firefox, WebKit).
- TestNG / JUnit: Often used alongside Selenium for managing test cases and generating reports.
- JMeter: Used for performance and load testing of web apps and APIs.
Key Differences Between Manual and Automation Testing
| Factor | Manual Testing | Automation Testing |
| Speed | Slower execution; requires human effort | Much faster; executes scripts instantly |
| Accuracy | Prone to human errors | Highly reliable and consistent |
| Cost | Lower upfront cost, but higher in the long run | Higher initial investment, but cost-effective over time |
| Coverage | Limited; hard to test large data sets manually | Wide test coverage including complex and repetitive scenarios |
| Tools | JIRA, TestRail, Zephyr | Selenium, Cypress, Playwright, JMeter, TestNG |
| Scalability | Hard to scale with large projects | Easily scalable with CI/CD pipelines |
When Should You Choose Manual Testing?
Although automation testing has proven to be an invaluable asset in many development cycles, manual testing still holds significant importance in certain scenarios. The flexibility, creativity, and human intuition involved in manual testing can uncover issues that automated scripts might miss, especially when working with user-centric aspects.
Here are the key situations when manual testing is the better choice:
Short-Term Projects
For minimum viable products (MVPs) or projects with shorter lifecycles, investing in the automation setup may not provide enough return on investment. Manual testing allows for quick validation without needing the resources to develop automated test scripts, making it ideal for projects where speed and agility are essential.
Frequent UI Changes
User interfaces in SaaS products or e-commerce websites often change as design updates and new features are introduced. Maintaining automation scripts for constantly evolving interfaces can become a costly and time-consuming task. Manual testing, on the other hand, allows testers to focus on visual elements and UI flow directly, adapting quickly to changes without the need for continuous updates to automation code.
Exploratory or Usability Testing
Manual testing is the go-to method for exploratory testing, where testers use their knowledge and creativity to explore the application, often without predefined test cases. This is crucial for identifying usability issues, user experience flaws, and edge cases that can’t be predicted by automated scripts. A tester’s ability to think critically and interact with the product as an end-user provides valuable insights into how the application will perform in the real world.
Tight Budget or Time Constraints
In cases where a project has a limited budget or a tight deadline, setting up an automated testing infrastructure may not be feasible. Manual testing is more economical for smaller projects or early-stage products, as it requires fewer resources to execute. For teams needing immediate feedback without the overhead of automation, manual testing becomes a practical and cost-effective option.
When Should You Choose Automation Testing?
Automation testing isn’t always the right fit for every situation. However, there are specific conditions where choosing automation can maximize efficiency, accuracy, and speed.
For Long-Term or Large-Scale Projects
If you’re building a large web app that will evolve over time with frequent updates, automation becomes a smart investment. In such cases, test cases are reused often, and manual testing can become tedious and slow. Automated scripts can run these repeated tests quickly and consistently.
Repetitive Regression Tests
Each time new features are added or changes are made, you need to ensure existing functionalities still work. This is known as regression testing. Automating these tests can save a lot of time and effort since they must be executed after every change or release.
CI/CD and Agile Environments
Modern development practices like Agile and Continuous Integration/Continuous Deployment (CI/CD) demand rapid and frequent testing. Automated tests can run instantly after code is committed, helping teams find bugs early and release faster.
High Test Coverage Needs
If your web app needs to be tested across many browsers, devices, or data combinations, automation provides scalability. It can execute hundreds of test cases in parallel, offering wider test coverage in less time compared to manual testing.
Accuracy and Consistency
Unlike manual testing, which is prone to human errors (especially in repeated tasks), automation ensures consistent and accurate results every time the test is run.
Cost and Time Considerations
Both manual and automated testing come with their own costs and time implications. Choosing between them often depends on your project’s budget, duration, and complexity.
Initial Setup Cost of Automation
Setting up automation testing requires time and investment. You need testing frameworks, skilled team members, and possibly tools like Selenium, Cypress, or Playwright. Writing scripts and maintaining them can take time initially.
Ongoing Effort in Manual Testing
While manual testing is easier and quicker to start, it demands ongoing effort every time new changes are made. Testers must re-run the same tests repeatedly, which becomes inefficient as the project grows.
Long-Term ROI Comparison
Even though automation has a higher setup cost, its long-term return on investment (ROI) is better for projects with frequent releases. You save time and effort in regression testing, reduce bugs in production, and speed up the delivery cycle.
Hidden Costs to Consider
Manual testing may result in delayed releases, missed bugs, and higher human effort. On the other hand, poorly maintained automation scripts can become flaky and require time for updates. Understanding these trade-offs helps you plan more effectively.
How to Strike the Right Balance (Hybrid Approach)
Instead of thinking manual vs automation, many teams adopt a hybrid testing strategy using both where they fit best.
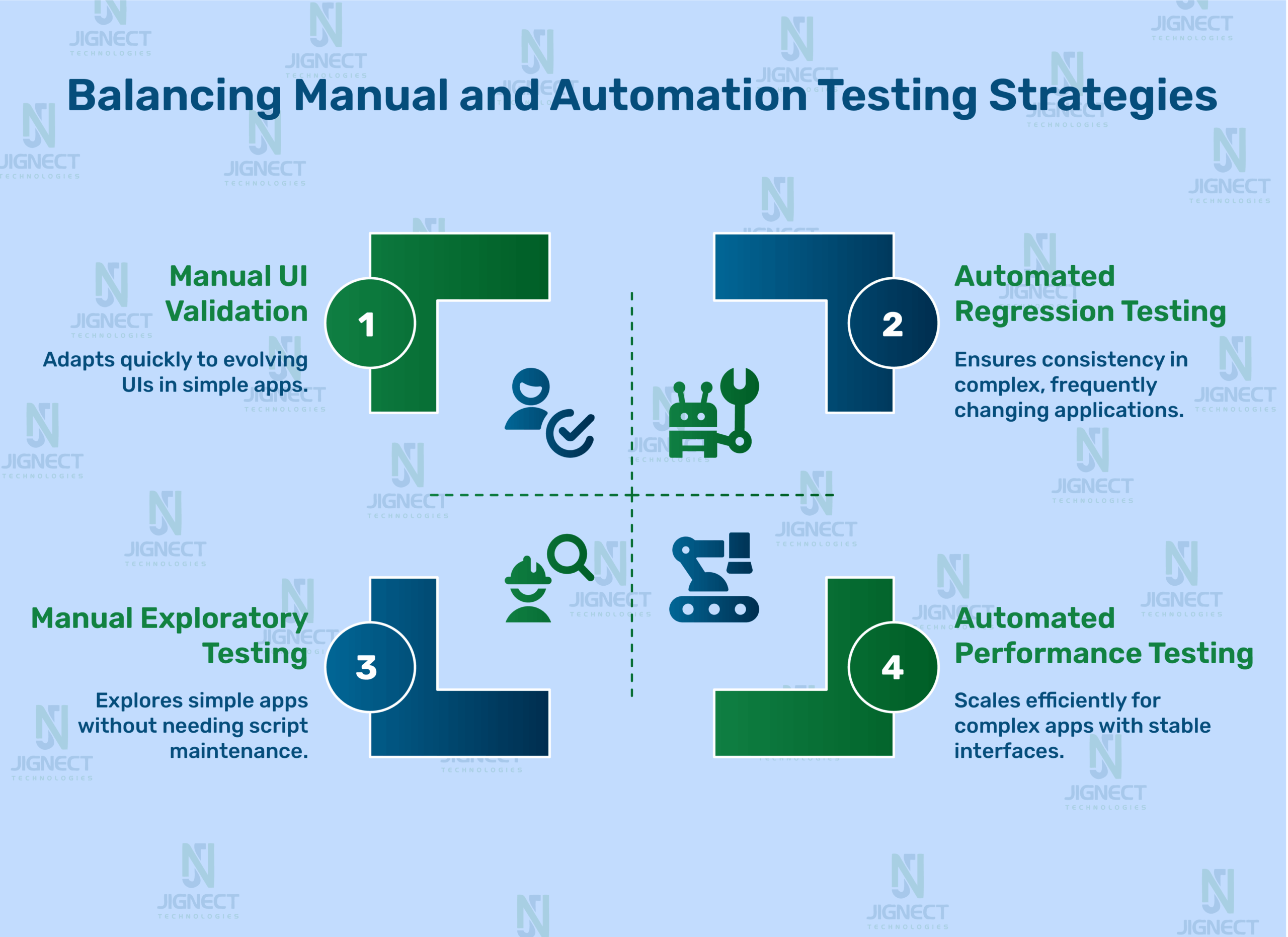
Manual Testing for Human-Centric Areas
Some tests require human observation like checking visual design, user experience, or exploratory testing. These tests are best performed manually. They help uncover unexpected bugs or usability issues that automated scripts might miss.
Automation for Repetitive Tasks
Tests like login functionality, form submissions, payment processing, and repeated regression cases can be automated. They don’t change often and are ideal for scripting once and running multiple times.
Best Practices for Hybrid Testing
- Use automation for stable, repetitive, and time-consuming test cases.
- Use manual testing for exploratory, ad-hoc, or visual tests.
- Plan automation based on ROI, frequency of test execution, and stability of features.
- Maintain both sets of tests with regular updates to avoid test failures or false results.
Real-World Scenario Example
Imagine you’re testing an online hotel booking platform:
- Automate the test cases for searching hotels, booking a room, applying promo codes, and verifying order history.
- Use manual testing to check how the booking calendar appears, test on different screen sizes, and explore edge cases like booking without login.
By combining both approaches, your team can deliver faster releases, better test coverage, and a high-quality user experience.
Factors to Consider When Deciding Between Manual and Automation Testing
When it comes to testing your web application, the right approach isn’t always black or white. Many elements influence the decision to go with manual, automation, or a hybrid strategy. Let’s dive into the most critical factors:
Project Timeline
If you’re working with a tight launch window or have short sprints, manual testing can be quicker to get started since it doesn’t require script development or environment setup. Manual testers can begin exploratory and functional testing almost immediately.
However, for long-term or continuous delivery models, automation testing becomes a clear winner. Once scripts are written, they can be run anytime, saving hours of manual work in regression testing.
Budget
One of the first questions startups ask is: “What will it cost?”
Manual testing typically has lower upfront costs since you’re only paying for testers’ time.
But automation comes with tools, frameworks, and skilled testers raising the initial investment.
However, over time, automated testing offers a better return on investment (ROI) by reducing repetitive manual work and catching issues earlier in the cycle, especially when integrated into CI/CD pipelines.
Tip: If you’re working with a tight budget, consider outsourcing to a software testing company for startups that provides affordable hybrid solutions.
Application Complexity
The more complex your app is, the more likely you’ll need automation:
- Apps with dynamic data flows
- Apps requiring backend validation
- Apps dependent on third-party integrations
- Scenarios that need frequent regression testing
Manual testing works well for small web apps or MVPs. But for multi-layered systems, automated testing ensures consistency, accuracy, and scale.
Team Expertise
Testing efficiency depends greatly on who’s doing it.
- Manual testing is easier to learn and quicker to implement for teams without deep QA knowledge.
- Automation testing, however, needs skilled professionals who understand scripting, test frameworks, and tools like Selenium, Cypress, Playwright, etc.
If your team lacks experience, hiring or outsourcing to an automation testing service provider India can ensure your testing pipeline is efficient and future-ready.
Test Maintenance Effort
One overlooked factor in automation is the maintenance burden.
Every time your UI or workflow changes, automation scripts might need updates. This adds overhead especially in fast-changing applications.
In contrast, manual testers can adapt on the fly without needing script refactoring.
This is why for applications with evolving UIs (like during design-heavy sprints), manual testing remains a good choice.
Balance tip: Use automation for regression, smoke, and performance testing. Use manual testing for UI validation and exploratory testing.
Conclusion: What’s Right for Your Web App?
There’s no universal answer to the question of manual vs automation testing.
Each method has strengths, and the best testing strategy is one that aligns with your project’s size, stage, goals, and resources.
Use manual testing if:
- You’re building a prototype or MVP
- The app has frequent UI changes
- Budget is tight
- You need exploratory or usability testing
Use automation testing if:
- Your app has a long development roadmap
- You’re practicing Agile or CI/CD
- Test cases are repetitive and stable
- You aim for faster releases with higher confidence
The ideal solution for most SaaS companies and web applications is a hybrid approach leveraging both manual and automation where each performs best.
Working with a QA outsourcing partner in India can give you the flexibility to scale testing without blowing your budget. You get access to skilled professionals, cost-effective services, and faster turnaround freeing up your internal teams to focus on innovation.
Witness how our meticulous approach and cutting-edge solutions elevated quality and performance to new heights. Begin your journey into the world of software testing excellence. To know more refer to Tools & Technologies & QA Services.
If you would like to learn more about the awesome services we provide, be sure to reach out.
Happy Testing 🙂